Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maruyama, Shuhei; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 205, p.110591_1 - 110591_13, 2024/09
Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Uritani, Akira*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1062, p.169227_1 - 169227_6, 2024/05
Yoshikawa, Ryuji; Imai, Yasutomo*; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Nuclear Technology, 210(5), p.814 - 835, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the study of safety enhancement on advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is essential to clarify the thermal-hydraulics under various operation conditions in a fuel assembly (FA) with the wire-wrapped fuel pins to assess the structural integrity of the fuel pin. A finite element thermal-hydraulics analysis code named SPIRAL has been developed to analyze the detailed thermal-hydraulics phenomena in a FA. In this study, the numerical simulations of the 37-pin bundle sodium experiments at different Re number conditions, including a transitional condition between laminar and turbulent flows and turbulent flow conditions, were performed to validate the hybrid turbulence model equipped in SPIRAL. The temperature distributions predicted by SPIRAL was consistent with those measured in the experiments. Through the validation study, the applicability of the hybrid turbulence model in SPIRAL to thermal-hydraulic evaluation of sodium-cooled FA in the wide range of Re number was confirmed.
 Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillation
Sr in highly radioactive aqueous samples via conversion to a kinetically stable 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid complex followed by concentration-separation-fractionation based on capillary electrophoresis-liquid scintillationOuchi, Kazuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Hirose, Kazuki*; Kurosawa, Yuika*; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Shibukawa, Masami*; Saito, Shingo*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1298, p.342399_1 - 342399_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0Given that conventional methods of high-dose sample analysis pose substantial exposure risks and generate large amounts of secondary radioactive waste, faster procedures allowing for decreased radiation emission are highly desirable. To address this need, we developed a  Sr
Sr quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed
quantitation technique that is based on liquid scintillation counting-coupled capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) with two-point detection and relies on the rapid concentration, separation, and fractionation of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-complexed  Sr
Sr in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify
in a single run. This method, which allows for the handling of high-dose radioactive specimens at the microliter level and is substantially faster than conventional ion-exchange protocols, was used to selectively quantify  Sr
Sr in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
in real high-dose waste. The successful concentration-separation in ctITP was ascribed to the inertness of the Sr-DOTA complex to dissociation.
Ito, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-026, 161 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been utilized as a method to quickly and extensively measure radiation distribution surrounding FDNPS. In order to utilize ARM and to promptly provide the results during a nuclear emergency, information on background radiation levels, topographical features, and controlled airspace surrounding nationwide nuclear facilities have been prepared in advance. In the fiscal year 2022, we conducted ARM around the Mihama Nuclear Power Station of Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO), the Tsuruga Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC), and the Ikata Power Station of Shikoku Electric Power Company (YONDEN), and prepared information on background radiation doses and controlled airspace. In addition, we have developed an aerial radiation detection system via unmanned airplane, which is expected to be an alternative to ARM, during a nuclear emergency. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Chang, L.-J.*; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112402_1 - 112402_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0The magnon excitation by ultrasound injection in Y Fe
Fe O
O is studied by inelastic neutron scattering. Both longitudinal and transverse ultrasound injections enhanced the inelastic neutron scattering intensity.
is studied by inelastic neutron scattering. Both longitudinal and transverse ultrasound injections enhanced the inelastic neutron scattering intensity.
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2023-022, 93 Pages, 2023/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple
, and X-rays" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple  -ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereinafter referred to as "SDM") was developed. In the research in 2022, we developed a code that handles measurement data of LSC, singles Ge, and 2D spectra (multiple
-ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereinafter referred to as "SDM") was developed. In the research in 2022, we developed a code that handles measurement data of LSC, singles Ge, and 2D spectra (multiple  ). In addition, to develop an integrated database, spectral data of 40 nuclides were obtained by actual measurements and simulation calculations.
). In addition, to develop an integrated database, spectral data of 40 nuclides were obtained by actual measurements and simulation calculations.
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 414, p.112574_1 - 112574_20, 2023/12
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 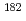 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1397 - 1405, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)The probability table method is a well-known method for addressing self-shielding effects in the unresolved resonance region. A long computational time is required to generate the probability table. The effective way to reduce the generation time of the probability table is the reduction of the number of ladders. The purpose of this study is the estimation of the optimal number of ladders using the statistical uncertainty in the probability table. To this end, the statistical uncertainty quantification method of the probability table was developed and the convergence behavior of the statistical uncertainty was investigated. The product of the probability table and the average cross section was considered the target of the statistical uncertainty. The convergence rate was affected by the average level spacing and reduced neutron width. The generation time of the probability table was less than half when the input parameter was changed from the number of ladders to the tolerance value.
Maruyama, Shuhei; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1372 - 1385, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Wakui, Takashi; Takagishi, Yoichi*; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Materials, 16(17), p.5830_1 - 5830_16, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Physical)Cavitation damage on the mercury target vessel is induced by proton beam injection in mercury. The prediction method of the cavitation damage using Monte Carlo simulations was proposed taking into account of the uncertainties of the position of cavitation bubbles and impact pressure distributions. The distribution of impact pressure attributed to individual cavitation bubble collapsing was assumed to be the Gaussian distribution, and the probability distribution of the maximum value of impact pressures was assumed to be three kinds of distributions; the delta function, the Gaussian and Weibull distributions. Two parameters were estimated using Bayesian optimization by comparing the distribution of the cavitation damage obtained from experiment with that of accumulated plastic strain obtained from the simulation. It was found that the results obtained using the Weibull distribution reproduced the actual cavitation erosion phenomenon better than the other results.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Hamaguchi, Shusuke*; Takata, Takashi*; Udagawa, Yutaka
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 411, p.112443_1 - 112443_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology) Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power PlantOta, Masakazu; Takahara, Shogo; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Nagakubo, Azusa; Hirouchi, Jun; Hayashi, Naho; Abe, Tomohisa; Funaki, Hironori; Nagai, Haruyasu
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 264, p.107198_1 - 107198_15, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)One of the current major radiation exposure pathways from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident-fallout is inhalation of the re-suspended  Cs occurring in air. While wind-induced soil particle resuspension has been recognized as a primary mechanism of
Cs occurring in air. While wind-induced soil particle resuspension has been recognized as a primary mechanism of  Cs resuspension, studies following the FDNPP accident suggested that fungal spores can be a significant source of the atmospheric
Cs resuspension, studies following the FDNPP accident suggested that fungal spores can be a significant source of the atmospheric  Cs particularly in the rural areas such as difficult-to-return zone (DRZ). To elucidate the relative importance of the two resuspension phenomena, we propose a model simulating resuspension of
Cs particularly in the rural areas such as difficult-to-return zone (DRZ). To elucidate the relative importance of the two resuspension phenomena, we propose a model simulating resuspension of  Cs as soil particles and fungal spores, and applied it to DRZ. Our model's calculation showed that soil particle resuspension was responsible for the surface-air
Cs as soil particles and fungal spores, and applied it to DRZ. Our model's calculation showed that soil particle resuspension was responsible for the surface-air  Cs observed during winter-spring, but could not account for the higher
Cs observed during winter-spring, but could not account for the higher  Cs concentrations observed in summer-autumn. The higher concentrations in the summer-autumn were in general reproduced by implementing fungal spore
Cs concentrations observed in summer-autumn. The higher concentrations in the summer-autumn were in general reproduced by implementing fungal spore  Cs emission, that replenished low soil particle
Cs emission, that replenished low soil particle  Cs resuspension in that period. According to our model's concept,
Cs resuspension in that period. According to our model's concept,  Cs accumulation in fungal spores and high spore emission rate characterized by the rural environment were likely responsible for the abundance of spore
Cs accumulation in fungal spores and high spore emission rate characterized by the rural environment were likely responsible for the abundance of spore  Cs in the air. It was inferred that the influence of the fungal spores on the atmospheric
Cs in the air. It was inferred that the influence of the fungal spores on the atmospheric  Cs would last longer since un-decontaminated forests still exist in DRZ.
Cs would last longer since un-decontaminated forests still exist in DRZ.
Ariyoshi, Gen; Saruta, Koichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Maeno, Koki*; Li, Y.*; Tsutsui, Kihei*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.1407 - 1420, 2023/08
Cavitation damage on a target vessel due to proton beam-induced pressure waves is one of the crucial issues for the pulsed neutron source using a mercury spallation target. As a mitigation technique for the damage, the helium microbubble injection into the mercury has been carried out by using a swirl bubbler in order to utilize compressibility of bubbles. Moreover, double-walled structure, which consists of an outer wall and an inner wall, has been applied as the target head structure. In this study, we aim to develop an abnormality diagnostic technology to detect the inner wall cracking, which is caused by such cavitation damage, from the outside of the target vessel. The mercury flow fields in the case with the cracking are evaluated by computational fluid dynamics analysis based on finite element method. And then, effect of the cracking on the flow field is discussed from the point of view of the flow-induced vibration and the acoustic vibration.
 sp
sp HRL
HRLSawada, Atsushi; Sakamoto, Kazuhiko*; Watahiki, Takanori*; Imai, Hisashi*
SKB P-17-06, 154 Pages, 2023/08
Takeda, Takeshi
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-007, 72 Pages, 2023/07
An experiment denoted as IB-HL-01 was conducted on November 19, 2009 using the Large Scale Test Facility (LSTF) in the Rig of Safety Assessment-V (ROSA-V) Program. The ROSA/LSTF experiment IB-HL-01 simulated a 17% hot leg intermediate break loss-of-coolant accident due to a double-ended guillotine break of pressurizer surge line in a pressurized water reactor (PWR). The break was simulated by a long nozzle upwardly mounted flush with a hot leg inner surface. The test assumptions included total failure of both high pressure injection system of emergency core cooling system (ECCS) and auxiliary feedwater system. In the experiment, relatively large size of break led to a fast transient of phenomena. The primary pressure steeply dropped after the break, and became lower than steam generator (SG) secondary-side pressure. Break flow turned from single-phase flow to two-phase flow soon after the break. Core uncovery started simultaneously with liquid level drop in downflow-side of crossover leg before loop seal clearing (LSC). The LSC was induced in both loops by steam condensation on accumulator (ACC) coolant of ECCS injected into cold legs. The whole core was quenched owing to the rapid recovery in the core liquid level after the LSC. Peak cladding temperature of simulated fuel rods was detected almost concurrently with the LSC. During the ACC coolant injection, liquid levels recovered in the hot legs and SG inlet plena because of liquid entrainment from the hot leg into the SG inlet plenum by high-velocity steam flow. After the continuous core cooling was confirmed through the actuation of low pressure injection system of ECCS, the experiment was terminated. This report summarizes the test procedures, conditions, and major observations in the ROSA/LSTF experiment IB-HL-01.
 Pt
Pt Al
Al
Ota, Kyugo*; Watabe, Yuki*; Haga, Yoshinori; Iesari, F.*; Okajima, Toshihiko*; Matsumoto, Yuji*
Symmetry (Internet), 15(8), p.1488_1 - 1488_13, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:60.94(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Koide, Kaoru
JAEA-Research 2023-003, 101 Pages, 2023/06
This study developed a geobotanical remote sensing method for estimating high water table areas such as groundwater discharge points using differences in the growth conditions of forest trees induced by moisture supply from groundwater in a humid warm-temperate forest area. A new vegetation index (VI) termed AgbNDVI (Added green band NDVI) was proposed to discriminate the differences. The AgbNDVI proved to be more sensitive to water stress on green vegetation than existing VIs: SAVI and EVI2, and possessed a strong linear correlation with the vegetation fraction. To validate the proposed method, a 23 km study area was selected in the Tono region of Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. The AgbNDVI values were calculated from atmospheric corrected SPOT HRV data. To correctly detect high VI points, the influence factors on tree growth were identified using the AgbNDVI values, DEM and forest type data; the study area was then divided into 555 segments according to combinations of the influence factors: elevation, slope gradient, slope aspect and forest type. Thresholds for detecting high VI points were defined for each segment based on a histogram of AgbNDVI values. By superimposing the high VI points on topographic and geologic maps, most of the high VI points are clearly located on the concave/convex slopes and near the geologic boundaries prone to groundwater runoff. In addition, field investigations support the correctness of the high VI points, because the growth increments and biomass of trees (
study area was selected in the Tono region of Gifu Prefecture, central Japan. The AgbNDVI values were calculated from atmospheric corrected SPOT HRV data. To correctly detect high VI points, the influence factors on tree growth were identified using the AgbNDVI values, DEM and forest type data; the study area was then divided into 555 segments according to combinations of the influence factors: elevation, slope gradient, slope aspect and forest type. Thresholds for detecting high VI points were defined for each segment based on a histogram of AgbNDVI values. By superimposing the high VI points on topographic and geologic maps, most of the high VI points are clearly located on the concave/convex slopes and near the geologic boundaries prone to groundwater runoff. In addition, field investigations support the correctness of the high VI points, because the growth increments and biomass of trees (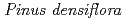 ) are greater than at points other than the high VI points, and they are located around known groundwater seeps and in a high water table area. Consequently, the proposed method can be expected to provide useful information for characterizing hydrogeological structures by combining with conventional photo-geological interpretation.
) are greater than at points other than the high VI points, and they are located around known groundwater seeps and in a high water table area. Consequently, the proposed method can be expected to provide useful information for characterizing hydrogeological structures by combining with conventional photo-geological interpretation.